[lwptoc]
Weight-loss Surgery
Am I a candidate for weight loss surgery?The only person you are destined to become is the person you decide to be. - Ralph Waldo Emerson
What is weight-loss surgery?
Weight-loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, refers to a group of surgical procedures that are performed to help people who are severely obese achieve significant and sustained weight loss and improve their overall health. These procedures alter the digestive system restricting the amount of food the patient can eat or reducing their body's ability to absorb calories, leading to significant weight loss, or both.
Why might weight-loss surgery be necessary? Being overweight has serious health effects, impacts quality of life, and can be frustrating when dieting fails. If you struggle with uncontrollable weight problems, it's important to understand obesity and morbid obesity as a disease, and the most effective treatment options, such as weight loss (bariatric) surgery. With a single operation, individuals can potentially experience improvement or resolution of multiple obesity-related medical conditions (comorbidities).
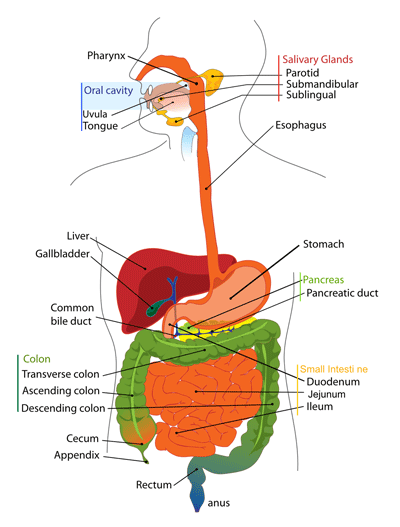

How does weight-loss surgery work?
Weight-loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, is a surgical procedure that involves modifying the stomach and/or the small intestine to reduce the amount of food that a person can consume and/or the amount of calories that are absorbed by the body. This change can impact the production and regulation of certain hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin, that are involved in regulating hunger and fullness. Ghrelin is often referred to as the ``hunger hormone`` because it stimulates appetite, while leptin is known as the ``satiety hormone`` because it signals the brain when the body is full. After weight-loss surgery, the hormonal changes can result in reduced hunger and increased feelings of fullness, which can help individuals eat less and potentially lose weight. This is one of the mechanisms through which weight-loss surgery can be effective in helping individuals achieve weight loss and manage their appetite, along with other important lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, and behavior modifications.
There are several types of weight-loss surgeries, each with their own method of achieving weight loss. Some of the most common weight-loss surgeries include:
Regardless of the specific surgery, weight loss occurs through a combination of factors:
It is important to note that weight-loss surgery is not a magic solution and requires significant lifestyle changes and adherence to a strict post-surgery diet and exercise plan. However, for many people struggling with obesity, weight-loss surgery can be an effective tool in achieving long-term weight loss and improving overall health.
How do you know if you are a candidate for weight-loss surgery?
Weight-loss surgery candidacy depends on each individual and their specific evaluation. However, each possible candidate will need to meet specific criteria to be accepted for a weight-loss surgery procedure. Besides the criteria listed below, many other factors will be considered by your physician such as age, metabolic, functional, and psychological state.
To use the BMI Calculator below, first convert your height and weight to metric units:
pounds
BMI Calculator Chart
| BMI | Weight Status |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 - 24.9 | Healthy |
| 25.0 - 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 - and Above | Obese |
Calculate Your BMI
BMI is only a surrogate measure of body fatness because it describes excess weight rather than excess body fat and does not take into account factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, and muscle mass. The Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) calculator generates the approximate number of calories your body burns per day at rest. Your BMR with activity factor is the approximated number of calories your body burns per day based on the activity factor you selected. Note: To convert inches to centimeters (cm), use the converter above or multiply your height in inches by 2.54, and to convert pounds to kilograms (kg) multiply your weight in pounds by 0.4536.

You're Not Alone!
The percentage of patients who undergo one of the four main types of weight-loss surgery can vary depending on the region, country, and year of analysis. However, here are some approximate percentages based on recent data. It's important to note that these percentages may vary depending on factors such as patient demographics, insurance coverage, and surgeon preference. It's always best to discuss the different types of weight-loss surgery with a qualified bariatric surgeon to determine the best option for your individual needs and goals.
Which medical weight-loss procedures and devices/products are approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and why is this important?
The FDA has approved several weight-loss surgeries such as gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, as well as devices such as the gastric balloon and gastric electric stimulator for weight loss. The FDA also approves weight-loss medications for the treatment of obesity. Each procedure and management device has its own benefits, risks, and weight loss results, and the best option for a patient will depend on their individual needs and goals.
You maybe asking, why do weight-loss surgery procedures need to be approved by the FDA, here are several important reasons:
Overall, the FDA's approval of weight-loss surgery procedures, devices, and products, helps to protect patient safety, ensure that patients receive effective treatment, and promote consistency and quality in the delivery of medical care.
FDA Approved Medical Weight Loss Procedures:
Click on the procedure below to view it’s description, and some pros and cons:
This procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving a small, tube-like section. The smaller stomach size leads to a feeling of fullness after eating smaller amounts of food, resulting in weight loss.
This surgery involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine to this pouch, which reduces the amount of food that can be consumed and the amount of calories that are absorbed.
This surgery involves placing a band around the top of the stomach to create a small pouch that can only hold a small amount of food.
This surgery involves removing a large portion of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to this smaller stomach pouch, similar to gastric bypass surgery. It also reroutes a portion of the small intestine, which reduces the amount of calories that are absorbed.
FDA Approved Medical Weight Loss Devices/Products:
Click on the procedure/device below to view it’s description, and some pros and cons:
This is a non-surgical procedure that involves placing a balloon in the stomach to create a feeling of fullness, which helps in reducing the amount of food intake. This device is approved by the FDA for people with a BMI of 30 or higher.
This is a non-surgical procedure that involves placing a tube in the stomach to drain a portion of the stomach contents after meals. This device is approved by the FDA for people with a BMI of 35 or higher.
This is a non-surgical procedure that involves suturing the stomach to create a smaller stomach pouch, which helps in reducing the amount of food intake. This device is approved by the FDA for people with a BMI of 30 or higher.
There are several FDA-approved prescription medications that can help in weight loss by suppressing appetite, increasing metabolism, or blocking the absorption of fat. These medications are approved for people with a BMI of 30 or higher, or a BMI of 27 or higher with obesity-related health problems.
What are the possible benefits and risks of weight-loss surgery?
When considering surgery to address severe obesity, the most important question is whether the benefits of the procedure outweigh the risks. Typically, the risks are incurred immediately during the surgery itself, while the benefits may take time to materialize through improved health, decreased risk of future illness, and an enhanced quality of life. Here we will explore some of the benefits and risks of surgical treatment for obesity.
Most Common Benefits of Surgical Treatment for Obesity:
Most Common Risks of Surgical Treatment for Obesity:
Surgical treatment for obesity can be an effective way to achieve significant and long-term weight loss, leading to improved overall health outcomes. However, it is essential to understand the risks associated with surgical treatment and to have a support system in place to manage the physical and emotional challenges that can arise. Ultimately, individuals should work with their healthcare provider to determine if surgical treatment for obesity is right for them.
What are the potential side effects associated with the different types of weight-loss surgery?
Weight-loss surgery is a significant step for individuals who are struggling with obesity and have not been able to achieve their weight loss goals through other means. However, like any surgical procedure, bariatric surgery carries some potential side effects and risks. Explore below, the potential side effects of each type of weight-loss surgery.
This procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach, leaving a small, tube-like section. The smaller stomach size leads to a feeling of fullness after eating smaller amounts of food, resulting in weight loss. Some of the potential side effects of this procedure include:
This surgery involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine to this pouch, which reduces the amount of food that can be consumed and the amount of calories that are absorbed. Some of the potential side effects of this procedure include:
This surgery involves placing a band around the top of the stomach to create a small pouch that can only hold a small amount of food. Some of the potential side effects of this procedure include:
This surgery involves removing a large portion of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to this smaller stomach pouch, similar to gastric bypass surgery. It also reroutes a portion of the small intestine, which reduces the amount of calories that are absorbed. Some of the potential side effects of this procedure include:
It is important to note that side-effects occur with any operation. Although they are less serious than complications, they may be permanent, and may require a change in lifestyle, to avoid continuing discomfort. These potential side effects are not experienced by all patients who undergo weight-loss surgery. Many patients are able to achieve significant weight loss and improve their overall health and quality of life without experiencing significant complications. However, it is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of weight-loss surgery with a qualified healthcare provider before making a decision.
What about insurance coverage and financial considerations of weight-loss surgery?
Another crucial aspect of this stage is understanding insurance coverage and financial considerations. The good news is bariatric surgery is covered by most insurance policies for the FDA approved weight-loss surgical procedures (gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch). In general, weight-loss surgery may be covered by insurance if it is deemed medically necessary by a qualified healthcare professional and meets the criteria for coverage outlined in the insurance policy. This typically requires documentation of significant health risks related to obesity and evidence that non-surgical weight loss methods have been unsuccessful.
It is important to note that insurance coverage for weight-loss surgery may also be subject to deductibles, co-pays, and other out-of-pocket expenses. You will need to work with your healthcare team to navigate insurance coverage, including understanding the costs associated with weight-loss surgery, potential out-of-pocket expenses, and any required documentation or paperwork. Many insurance companies have a mandatory (multi-month) physician supervised weight management protocol that you must complete before surgery.

Some patients choose to pay for the operation themselves. Providers will offer special packages for cash patients, which include all usual services, at a substantial discount. The actual rate varies, depending on the type of surgery chosen, and initial weight and health status.
What medical insurance covers weight-loss surgery?
Overall, the coverage for weight-loss surgery varies depending on the type of insurance and individual plan. It is important to understand the coverage options and requirements for your specific insurance plan and to work closely with your healthcare provider and insurance provider to navigate the process. In the US, the average cost of bariatric surgery can range from $15,000 to $35,000 or more, depending on the type of procedure, location, and other factors. However, it’s important to note that these costs are approximate and can vary significantly. Weight-loss surgery, like any surgery, comes with a range of costs that patients should be aware of before making a decision. Here are some of the costs associated with weight-loss surgery:
Before surgery:
- Consultation fees with a bariatric surgeon or weight-loss specialist
- Diagnostic testing such as blood work, EKG, and imaging tests
- Pre-operative dietitian visits and nutritional supplements
During surgery:
- Hospital fees for the operating room and recovery room
- Surgeon’s fees
- Anesthesiologist’s fees
After surgery:
- Follow-up appointments with the surgeon and other specialists such as a dietitian or psychologist
- Nutritional supplements and medication
- Cost of any complications that may arise
- Cost of support services, such as a gym membership or weight loss support group
In addition to these costs, patients should also consider any time off work that may be required for the surgery and recovery period, as well as the potential long-term costs of maintaining weight loss through lifestyle changes.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) and general answers for those considering weight-loss surgery.
You may want to make note of these questions to ask your Doctor during your consultation:
How long will it take to recover from weight-loss surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery you have and your individual circumstances. In general, patients can expect to spend one to three days in the hospital after surgery and may need up to six weeks to fully recover.
Will I need to make changes to my diet after weight-loss surgery?
Yes, you will need to make significant changes to your diet after weight-loss surgery. Your doctor or a registered dietitian will provide you with detailed instructions on what you can and cannot eat.
Will I need to exercise after weight-loss surgery?
Yes, regular exercise is an important part of maintaining your weight loss and improving your overall health after surgery. Your doctor will provide you with guidelines for safe and effective exercise.
How long will it take to see the benefits of weight-loss surgery?
While the initial weight loss can be significant, it can take several months to a year to see the full benefits of weight-loss surgery. This includes improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
Can weight-loss surgery be reversed?
In some cases, weight-loss surgery can be reversed, but it is generally considered a last resort. Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of surgery reversal with you.
Will insurance cover the cost of weight-loss surgery?
Many insurance plans do cover the cost of weight-loss surgery, but coverage varies depending on the individual plan. It is important to check with your insurance provider to determine your coverage and any out-of-pocket costs you may be responsible for.
What should I expect prior to weight-loss surgery?
What to expect before, during, and after the procedure:
Before weight-loss surgery, your doctor will evaluate your health history, perform a physical exam, and order blood tests, imaging scans, and other diagnostic tests to determine if you are a candidate for weight-loss surgery. You may also be required to participate in a weight-loss program to prepare for surgery and achieve a healthy weight range. During the surgery, you will be under general anesthesia, and the procedure will take several hours, depending on the type of surgery you undergo. After surgery, you will need to follow a strict diet and exercise plan, attend regular follow-up appointments with your doctor, and take medications as prescribed to manage pain, prevent infection, and promote healing.
How do I choose the right weight-loss surgery?
There are several types of weight-loss surgery, including gastric bypass, gastric sleeve, adjustable gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Each surgery has its pros and cons, and the best option for you will depend on your individual needs and health status. For example, gastric bypass may be a good choice for those with type 2 diabetes, while gastric sleeve may be better for those with a higher BMI. Your doctor will help you choose the best option based on your medical history, goals, and other factors.
What changes should I expect in my eating habits, exercise routine, and overall lifestyle?
After weight-loss surgery, you will need to make significant changes to your lifestyle. Your diet will consist of small, frequent meals of nutrient-dense foods, and you will need to avoid high-fat, high-sugar, and processed foods. You will also need to establish an exercise routine, gradually increasing your activity level as you heal. Other changes may include adjusting to a new body size, managing emotional changes, and addressing any potential complications from surgery.
What are some of the potential complications after weight-loss surgery and how can they be managed?
Although weight-loss surgery is generally safe, there are potential complications that can arise, such as infection, bleeding, and blood clots. Other complications may include hernias, bowel obstruction, and nutritional deficiencies. To manage these complications, it is important to attend regular follow-up appointments with your doctor, report any symptoms or issues promptly, and follow a strict post-operative diet and exercise plan.
How can I get emotional support before and after weight-loss surgery? What resources are available to help me cope with the changes I'll experience?
Emotional support is a critical component of weight-loss surgery success. Before surgery, you may benefit from counseling or support groups to address any emotional issues related to obesity. After surgery, you may experience emotional changes related to your new body size, eating habits, and other lifestyle changes. Support groups, counseling, and online communities can be valuable resources to help you cope with these changes and stay motivated to achieve your health goals.
What weight-loss surgery procedures are covered by insurance and how can I navigate the insurance process?
Insurance coverage for weight-loss surgery varies by insurance provider and plan. Some insurance plans may cover all or part of the cost of surgery, while others may require pre-approval or have strict eligibility requirements. It is important to work with your insurance provider to understand your coverage options and navigate the insurance process.
How can I maintain my weight loss after surgery and avoid regaining weight?
Maintaining weight loss after surgery requires ongoing commitment to a healthy lifestyle. This may include continued exercise, a healthy diet, and regular follow-up appointments.
What types of physical activities are safe and effective after weight-loss surgery?
After weight-loss surgery, follow your Doctor’s instructions, but generally, it is important to start with light physical activity, such as walking, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise. A combination of aerobic exercise and strength training is recommended to build muscle and burn fat. The recommended amount of exercise after weight-loss surgery is at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity exercise. To make exercise a regular part of your routine, it can be helpful to find an activity that you enjoy and to schedule it into your daily or weekly routine.
What types of nutrition and diet are safe and effective after weight-loss surgery?
After weight-loss surgery, it is important to follow your Doctor’s instructions, but generally a diet that is high in protein, low in fat and sugar, and nutrient-dense. This often means eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day, focusing on lean protein sources, and avoiding processed or high-calorie foods. It is also important to stay hydrated and take a multivitamin to ensure adequate nutrient intake. Different types of diets, such as low-carb or low-fat, may be recommended depending on individual health needs and weight loss goals.
What are the financial considerations of undergoing weight-loss surgery?
The costs associated with weight-loss surgery can vary depending on factors such as the type of surgery, location, and insurance coverage. It is important to research and understand the costs associated with the surgery, as well as any ongoing costs such as follow-up appointments or dietary supplements. Some insurance plans may cover the cost of weight-loss surgery, and there may be financial assistance programs available for those who are uninsured or underinsured.
What special considerations should I be aware of when considering weight-loss surgery?
There are a number of special considerations that you should be aware of when considering weight-loss surgery. These include:
- Existing health conditions: If you have existing health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or sleep apnea, you may need to take extra precautions before and after surgery. Your surgeon will work with you to develop a plan that takes into account any health conditions you may have.
- Medications: Some medications can interfere with the effectiveness of weight-loss surgery or increase your risk of complications. It’s important to talk to your doctor about any medications you are taking before considering surgery.
- Age: Age can be a factor in determining whether weight-loss surgery is a good option for you. While there is no upper age limit for surgery, older patients may be at higher risk for complications.
- Mental health: Your mental health is an important consideration when deciding whether weight-loss surgery is right for you. If you have a history of mental health issues such as depression or anxiety, you may need to work with a mental health professional before and after surgery to ensure you have the support you need.
- Pregnancy: If you are planning to become pregnant, you may need to delay weight-loss surgery until after your pregnancy. Pregnancy can also affect the effectiveness of weight-loss surgery, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about your plans.
- Follow-up care: Weight-loss surgery is not a one-time solution. It requires ongoing follow-up care, including regular visits with your surgeon, a dietitian, and possibly a mental health professional. You should be prepared to commit to this ongoing care in order to ensure the best possible outcomes.
A pathway to a healthier life!
Weight-loss surgery is an effective option for those struggling with obesity and its associated health risks. However, it should not be viewed as a quick fix, but rather as a tool to aid in weight loss and a healthier lifestyle. It is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of action and to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of each weight-loss surgery option. Additionally, it is important to remember that weight loss surgery is just one part of the equation, and a commitment to healthy eating habits and regular exercise is essential for long-term success. With proper care and management, weight loss surgery can provide a pathway to a healthier life.



